[Design Pattern] Composition Pattern
Composition Pattern이란?
컴포지트 패턴(Composite pattern)이란
객체들의 관계를 트리 구조로 구성하여 부분-전체 계층을 표현하는 패턴으로,
사용자가 단일 객체와 복합 객체 모두 동일하게 다루도록 하는 패턴입니다.
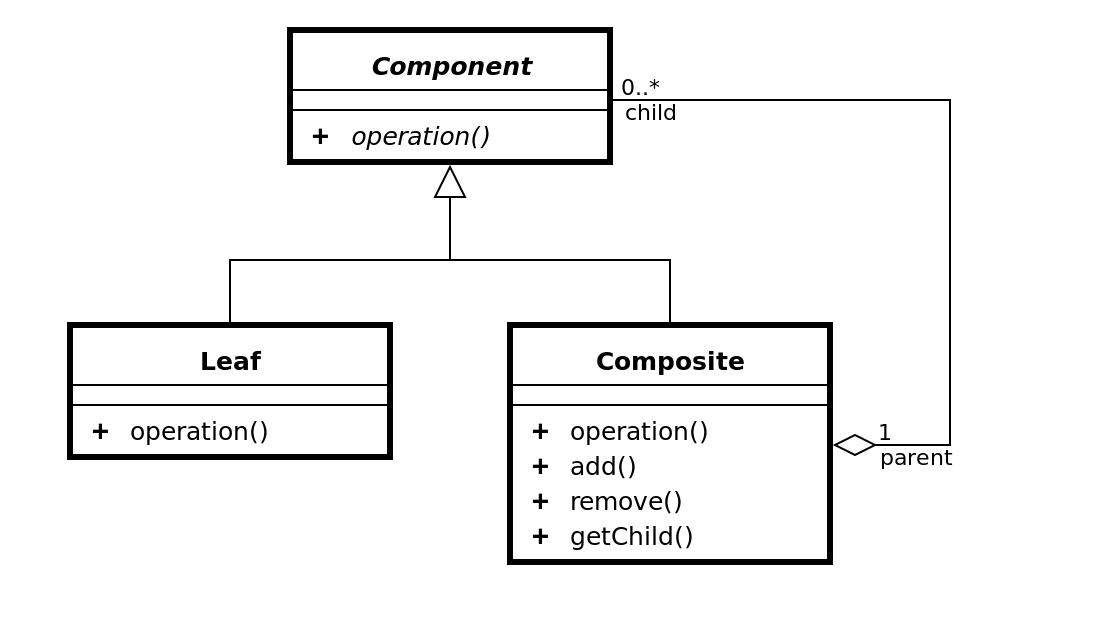
- component
- 컴포지션의 모든 개체에 대한 기본 인터페이스입니다.
- 하위 컴포지트를 관리하는 공통 메서드가 있는 인터페이스 또는 추상 클래스 여야 합니다.
- 즉, Leaf 클래스와 전체에 해당하는 Composite클래스의 공통 인터페이스를 작성합니다,
- leaf
- 기본 구성 요소의 기본 동작을 구현합니다. 다른 객체에 대한 참조는 포함되어 있지 않습니다.
- 구체적인 부분 클래스
- Composite 객체의 부품으로 설정합니다.
- composite
- 전체 클래스입니다.
- Leaf를 요소로 가집니다.
- 복수개의 Leaf, 복수개의 Composite객체를 부분으로 가질 수 있습니다.
- client – 기본 구성 요소 개체를 사용하여 컴포지션 요소에 액세스 할 수 있습니다.
Composition Pattern with Java
ex1) Graphic
/** "Component" */
interface Graphic {
public void print();
}
/** "Composite" */
class CompositeGraphic implements Graphic {
private List<Graphic> mChildGraphics = new ArrayList<Graphic>();
public void print() {
for (Graphic graphic : mChildGraphics) {
graphic.print();
}
}
public void add(Graphic graphic) {
mChildGraphics.add(graphic);
}
public void remove(Graphic graphic) {
mChildGraphics.remove(graphic);
}
}/** "Leaf" */
class Ellipse implements Graphic {
public void print() {
System.out.println("Ellipse");
}
}public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ellipse ellipse1 = new Ellipse();
Ellipse ellipse2 = new Ellipse();
Ellipse ellipse3 = new Ellipse();
Ellipse ellipse4 = new Ellipse();
CompositeGraphic graphic = new CompositeGraphic();
CompositeGraphic graphic1 = new CompositeGraphic();
CompositeGraphic graphic2 = new CompositeGraphic();
graphic1.add(ellipse1);
graphic1.add(ellipse2);
graphic1.add(ellipse3);
graphic2.add(ellipse4);
graphic.add(graphic1);
graphic.add(graphic2);
//Prints the complete graphic (four times the string "Ellipse").
graphic.print();
}
}ex2) Computer
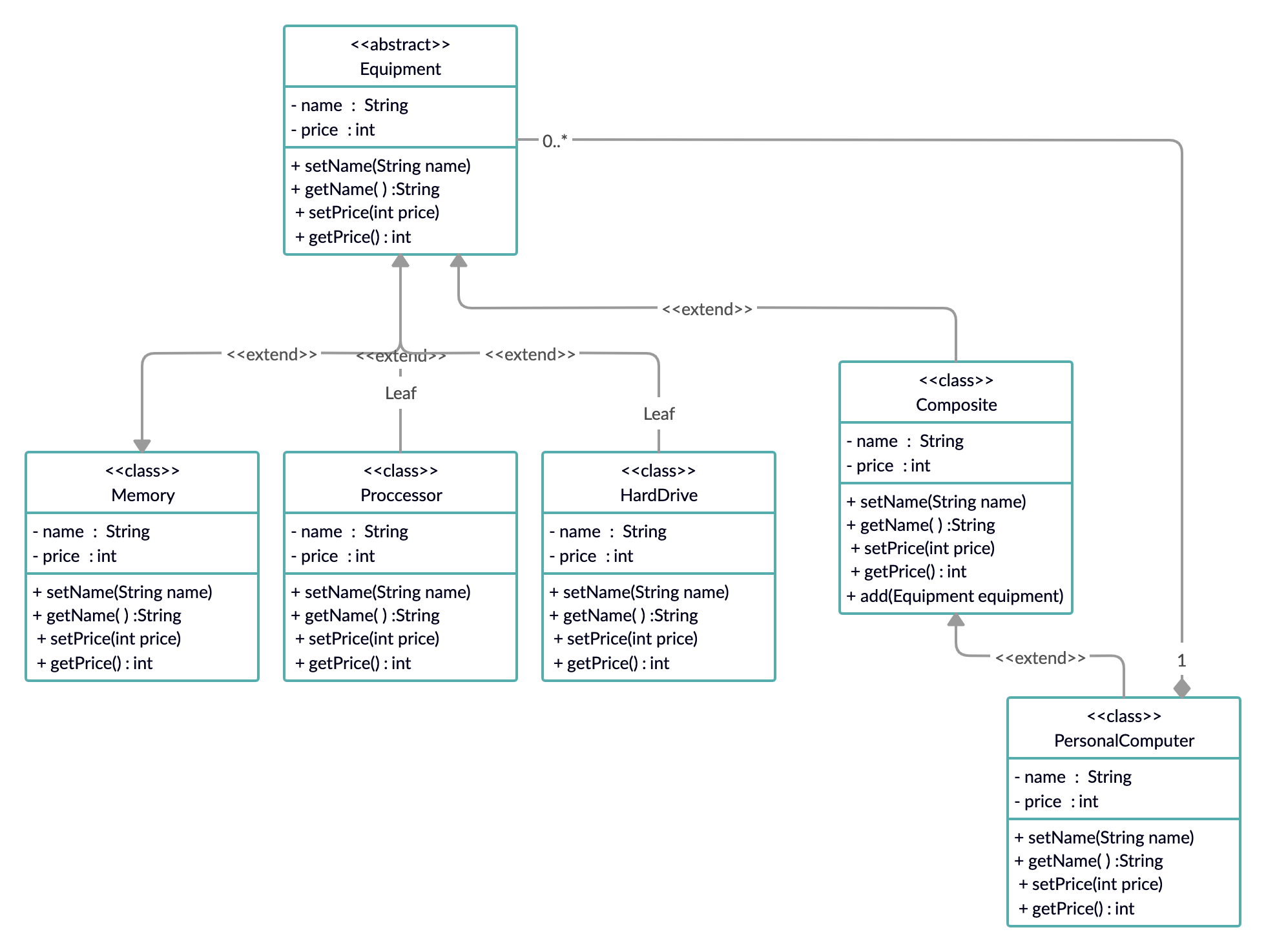
Memory , Proccessor, HardDrive는 Leaf입니다.
Leaf와 Composite는 component(Equipment)를 상속합니다.
Composite를 상속하는 PersonalComputer는 여러 개의 Leaf 혹은 복수개의 composite를 가질 수 있습니다.
public abstract class Equipment {
private int price;
private String name;
Equipment(int price, String name) {
this.price = price;
this.name = name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}public class HardDrive extends Equipment {
public HardDrive(int price, String name) {
super(price, name);
}
}
public class Processor extends Equipment {
public Processor(int price, String name) {
super(price, name);
}
}
public class Memory extends Equipment {
public Memory(int price, String name) {
super(price, name);
}
}
public class Composite extends Equipment {
ArrayList<Equipment> equipments = new ArrayList<>();
Composite(String name) {
super(0, name);
}
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.N)
@Override
public int getPrice() {
return equipments.stream()
.map(Equipment::getPrice)
.mapToInt(p -> (int) p)
.sum();
}
public void add(Equipment equipment) {
equipments.add(equipment);
}
}public class PersonalComputer extends Composite {
public PersonalComputer(String name) {
super(name);
}
}public class CompositeTest {
@Test
public void compositionTest() {
PersonalComputer pc = new PersonalComputer("PC");
pc.add(new Processor(1000, "Intel"));
pc.add(new Memory(500, "8GB"));
pc.add(new HardDrive(800, "SSD"));
Assert.assertThat(pc.getName(), CoreMatchers.is("PC"));
Assert.assertThat(pc.getPrice(), CoreMatchers.is(2300));
}
}
Composition Pattern with Kotlin
ex1) 컴퓨터
open class Equipment(
open val price: Int,
val name: String
)
open class Composite(name: String) : Equipment(0, name) {
private val equipments = ArrayList<Equipment>()
override val price: Int
get() = equipments.map { it.price }.sum()
fun add(equipment: Equipment) =
apply { equipments.add(equipment) }
}
/** Composite*/
class PersonalComputer : Composite("PC")
/** Leaf*/
class Processor : Equipment(1070, "Processor")
/** Leaf*/
class Memory : Equipment(280, "Memory")
/** Leaf*/
class HardDrive : Equipment(250, "Hard Drive")
class CompositeTest {
@Test
fun Composite() {
val pc = PersonalComputer()
.add(Processor())
.add(HardDrive())
.add(Memory())
println(pc.price)
assertThat(pc.name).isEqualTo("PC")
assertThat(pc.price).isEqualTo(1600)
}
}ex2) 플레이
interface IMedia {
fun play()
fun displaySubtitle()
fun setPlaySpeed(speed:Float)
fun getName() :String
}class Movie(val title:String): IMedia {
private var speed = 1f
override fun play() {
println("Now playing: ${title}...")
}
override fun displaySubtitle() {
println("display subtitle")
}
override fun setPlaySpeed(speed:Float) {
this.speed = speed
println("current play speed set to: $speed")
}
override fun getName(): String {
return title
}
}
class PlayList(val title:String): IMedia {
var movieList:MutableList<IMedia> = mutableListOf()
fun addNewMedia(media: IMedia) = movieList.add(media)
fun removeMedia(media: IMedia){
movieList = movieList.filter{ it.getName() != media.getName() }.toMutableList()
}
override fun play() {
movieList.forEach { it.play() }
}
override fun displaySubtitle() {
println("display certain subtitle")
}
override fun setPlaySpeed(speed: Float) {
movieList.forEach { it.setPlaySpeed(speed) }
}
override fun getName(): String {
return title
}
}fun main() {
val actionMoviePlayList =
PlayList("Action Movies")
val movieB: IMedia =
Movie("The Dark Knight")
val movieC: IMedia =
Movie("Inception")
val movieD: IMedia =
Movie("The Matrix")
actionMoviePlayList.apply {
addNewMedia(movieB)
addNewMedia(movieC)
addNewMedia(movieD)
}
val dramaPlayList =
PlayList("Drama Play List")
val movie1: IMedia =
Movie("The Godfather")
val movie2: IMedia =
Movie("The Shawshank Redemption")
dramaPlayList.apply { addNewMedia(movie1);addNewMedia(movie2) }
val myPlayList = PlayList("My Play List")
myPlayList.apply {
addNewMedia(actionMoviePlayList)
addNewMedia(dramaPlayList)
}
myPlayList.play()
}Movie : Leaf
Compotie : PlayList
정리
Composite Pattern은
단일 객체와 복합 객체를 동일하게 컨트롤할 수 있게끔 도와주는 패턴이다.
컴포지트 패턴은 3가지의 요소에 의해 이루어진다.
Component, Leaf, Composite
샘플 보러 가기
https://github.com/qjatjr1108/DesignPattern
qjatjr1108/DesignPattern
DesignPattern Sample. Contribute to qjatjr1108/DesignPattern development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
참고
https://blog.seotory.com/post/2017/09/java-composite-pattern
'DesignPattern' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Design Pattern] Strategy Pattern (4) | 2019.10.11 |
|---|---|
| [Design Pattern] Flyweight pattern (4) | 2019.10.10 |
| [Design Pattern] Bridge Pattern (4) | 2019.10.10 |
| [Design Pattern] Proxy Pattern (4) | 2019.10.08 |
| [Design Pattern] Decorator Pattern (2) | 2019.10.08 |


댓글